What is the function of Wire Connectors?
2025-12-04 03:36Wire Harness Connectors: The Invisible Pillars of Modern Technology
Wire harness connectors are ubiquitous yet often overlooked, serving as the indispensable "joints" and "bridges" within modern electrical systems. They prevent damage from incorrect wiring and ensure the orderly transmission of complex signals, such as data buses.
II. Where Do They "Work Silently"?
Wire harness connectors are the invisible pillars supporting modern society, working diligently across numerous fields:
Automotive Industry: A modern vehicle contains hundreds of wire harnesses stretching kilometers and thousands of connectors. Everything from airbags and ABS brakes to infotainment systems relies on them. Electric vehicles, in particular, require special high-voltage, high-current connectors for the battery pack, motor, and charging interface.
Consumer Electronics: Flexible Printed Circuit (FPC) connectors linking a smartphone's mainboard to its screen and battery enable sleek, lightweight designs and repairability.
Industrial & Energy Sectors: In factory automation equipment, robotics, and wind turbines, connectors must endure constant vibration and extreme temperatures to ensure uninterrupted operation.
Medical Equipment: Connectors in life-support monitors and imaging devices must guarantee absolute reliability, meeting stringent requirements for biocompatibility and sterilization.
Aerospace & Aviation: Connectors here represent the pinnacle of engineering, demanding extreme lightweight design, reliability, and performance in harsh environments like vacuum and ultra-low temperatures.
III. How to Choose the Right Connector?
With thousands of types available, the key to selection lies in precise matching:
Electrical Parameters Are Fundamental: First, determine whether you need to transmit high current (power) or high-speed signals (data), and identify the required current, voltage, and signal frequency.
Match Physical & Environmental Needs: Consider the available space, required mating cycles, operational temperature, humidity, and exposure to oils or water. This determines the connector's shape, size, locking mechanism, and protection level (e.g., IP67 for waterproofing).
Industry Standards & Certifications: Sectors like automotive and medical have strict standards (e.g., USCAR for automotive, ISO 13485 for medical). Always choose products with compliant certifications.
Cost & Supply Chain: Balance the project budget while meeting performance requirements, and consider the long-term stability of the supply chain.
Connector types are diverse and can be categorized from different perspectives. From the most practical angles—form factor/application, core electrical function, and industry-specific use—here are the main types and their primary roles.

IV. What Are the Different Types of Connectors?
Categorized by Form Factor, Structure & Core Application (Most Common)
This is the most intuitive classification, directly linked to installation scenarios and physical requirements.
| Type | Core Shape & Characteristics | Primary Function & Application Scenarios |
|---|---|---|
| Circular Connectors | Cylindrical housing, often with a threaded locking mechanism. | Provide excellent sealing, vibration resistance, and reliability. Commonly used in harsh environments such as industrial machinery, automotive exteriors (sensors, lights), aerospace, and outdoor equipment requiring high dust/water protection (IP ratings). |
| Rectangular/Trapezoidal Connectors | Square or polygonal housing with densely arranged contact pins. | Enable high-density, multi-pin signal and power transmission. Primarily used for internal board-to-board connections, industrial control cabinets, medical instruments, servers, and other space-constrained applications requiring numerous connections. |
| PCB Connectors | Soldered or surface-mounted directly onto Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs). | Act as the "bridge" between the circuit board and external wiring or another PCB. They are foundational to all electronic devices, used for motherboard power delivery, signal I/O, and module expansion. |
| RF (Radio Frequency) Connectors | Typically feature a circular coaxial structure for transmitting high-frequency signals. | Specifically designed for transmitting high-frequency RF signals, ensuring signal integrity, low loss, and shielding. Used in communication equipment (e.g., base stations), wireless networks, test instruments, and antenna systems. |
| Fiber Optic Connectors | Employ precision ceramic ferrules for aligning and connecting optical fibers. | Facilitate precise alignment and low-loss transmission of optical signals. Used in fiber optic communication networks, data centers, high-definition video transmission, and medical laser equipment. |
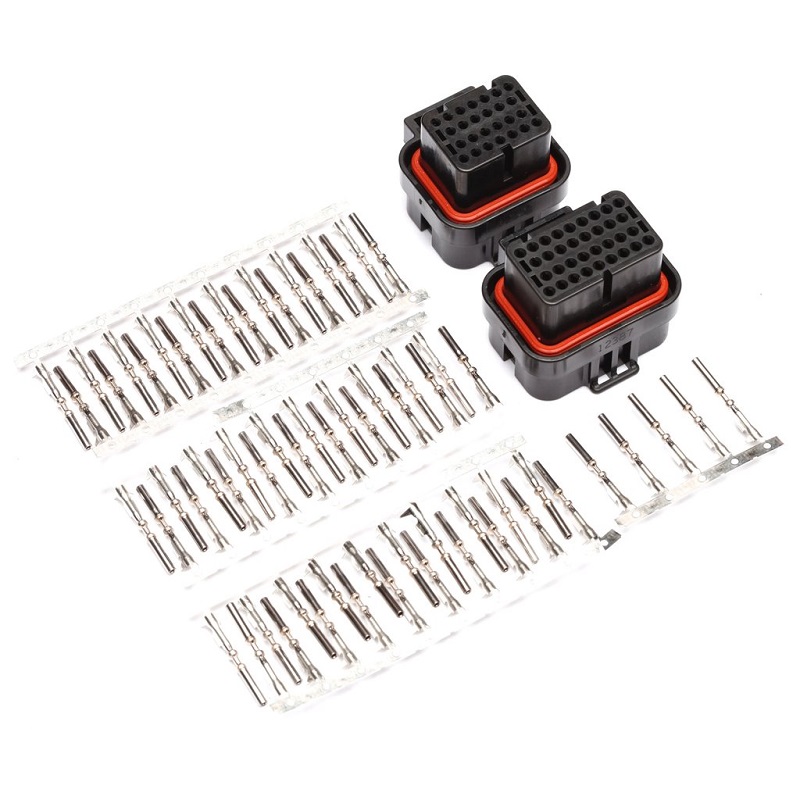

V.Choosing the Correct Wire Harness Terminal: Insulated vs. Non-Insulated
Selecting the appropriate terminal is a critical step in wire harness design, directly impacting the safety, durability, and reliability of the electrical connection. The choice hinges on a thorough analysis of the circuit requirements and the specific application environment. A fundamental distinction lies in choosing between insulated and non-insulated terminals.
1. Insulated Terminals: For Demanding Environments
Insulated terminals feature a protective plastic or nylon sleeve that encases the metal crimp barrel. This layer provides crucial benefits:
Environmental Protection: Shields the connection from moisture, dust, chemicals, and accidental short-circuiting caused by contact with other metal parts or wires.
Enhanced Safety: Provides basic touch protection and improved strain relief.
Corrosion Resistance: Helps prevent oxidation at the connection point.
Recommended Use: Ideal for harsh or unpredictable environments such as automotive engine bays, industrial machinery, outdoor equipment, and any area with exposure to fluids, vibrations, or contaminants.
2. Non-Insulated (Bare) Terminals: For Controlled, Internal Applications
Non-insulated terminals consist solely of the metal contact (e.g., copper, tin-plated copper). Their characteristics include:
Cost-Effectiveness: Generally more economical due to simpler construction.
Compact Size: Allow for higher-density connections in tight spaces.
Inspection Ease: The crimp connection is fully visible for quality verification.
Recommended Use: Suited for protected, dry, and controlled environments inside enclosed panels, cabinets, or devices where there is no risk of moisture, corrosion, or accidental contact.
Making the Right Choice
The decision should follow this logical flow:
Step 1: Assess the Environment. Is it harsh, exposed, or stable and protected?
Step 2: Define the Requirements. Is corrosion resistance, electrical insulation, or cost a primary driver?
Step 3: Select the Type. Opt for insulated terminals for durability in demanding conditions. Choose non-insulated terminals for cost-sensitive, internal applications with minimal environmental stress.
A professional wire harness manufacturer can provide invaluable guidance in this selection process, ensuring your terminals meet all mechanical, electrical, and environmental specifications for a long-lasting and secure connection.
We sincerely invite you to collaborate with Kehan Electronics for your next custom wiring project. Contact us today to obtain professional technical support and customized solutions, ensuring optimal performance and long-term reliability.
