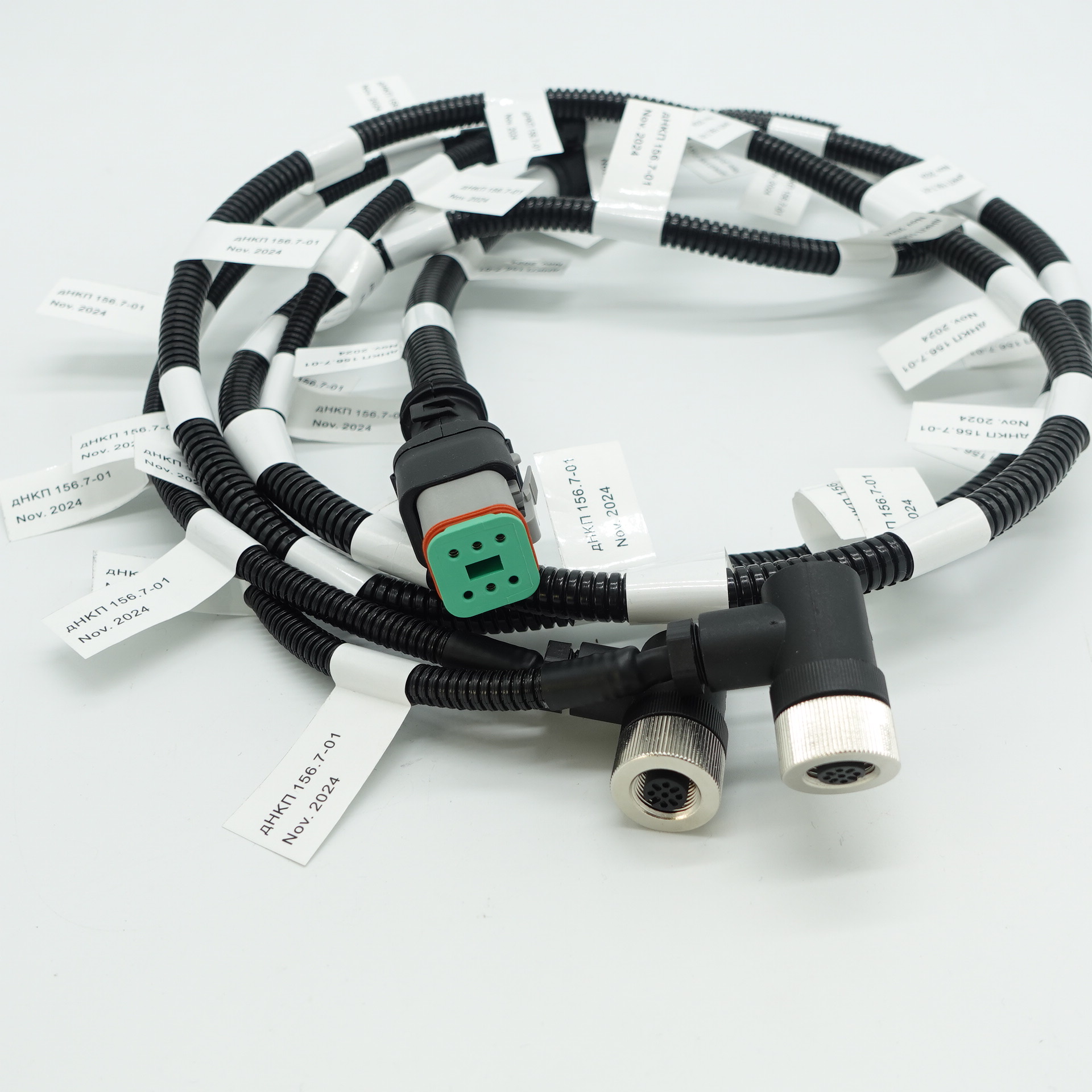
How does the wiring harness factory ensure product quality?
2025-12-19 19:15The Ultimate Guide to Wire Harness Crimping Standards: Ensuring Reliability & Quality
For any business involved in electronics, automotive, aerospace, or industrial manufacturing, understanding and adhering to wire harness crimping standards is non-negotiable. These standards define the precise methods for creating reliable mechanical and electrical connections between wires and terminals. For your independent brand, demonstrating expertise in these protocols is a powerful way to build professional trust with global clients.
This guide breaks down the multi-layered framework of crimping standards, from universal guidelines to industry-specific mandates.
1. Universal Process Standards (The Industry Foundation)
These are the globally recognized benchmarks that establish the fundamental quality criteria for crimp connections.
IPC/WHMA-A-620: The undisputed "Acceptability Standard for Cable and Wire Harness Assemblies." It is the essential reference for any wire harness assembly process. This standard provides clear visual and mechanical criteria for crimped connections across three grades:
Key Benefit: Offers a common "language" for quality acceptance between customers and manufacturers, preventing disputes.
Target (Ideal): The perfect outcome.
Acceptable (Process Indicator): Meets minimum requirements for a reliable connection.
Defect (Process Defect): Fails requirements and must be reworked or rejected.
It covers critical crimp quality aspects like wire placement, insulation support, bell mouth, and conductor strand distribution.
2. Industry & Application-Specific Standards
These rigorous standards build upon universal ones, adding extreme requirements for reliability, durability, and safety in critical fields.
Automotive Industry:
IATF 16949: The core Quality Management System standard mandating rigorous process control for automotive wire harness manufacturing.
LV Standards (e.g., LV 214, LV 112): Developed by the German Automotive Industry Association (VDA), these are among the strictest. They specify exact requirements for terminal crimping, including dimensions, mechanical performance (pull-out force), electrical performance (voltage drop), and environmental testing (salt spray, thermal shock).
USCAR Standards: The North American counterpart, serving as a key compliance gateway for automotive suppliers.
Aerospace Industry:
SAE AS50881: The leading global standard for aerospace wiring systems, detailing comprehensive design, manufacturing, and testing requirements for flight-critical cable assemblies.
Military & Defense:
3. Core Electrical & Mechanical Performance Metrics
Adherence to any standard translates into measurable, verifiable parameters:
Crimp Pull-Force / Tensile Strength: The minimum force required to extract a wire from its crimped terminal. This is the primary proof of mechanical connection integrity.
Voltage Drop: The voltage loss across the crimp when carrying a specified current. This is the key indicator of electrical connection quality. A low voltage drop signifies low resistance, minimal heat generation, and high efficiency.
Crimp Height and Width: The most critical process-controlled dimensions. Must be measured with calibrated micrometers and kept strictly within the terminal manufacturer's specified tolerance range. Incorrect crimp height is a leading cause of connector failure.
Visual & Structural Inspection:
Bell Mouth: A slight flare at the wire barrel's entry and exit points to prevent cutting the conductor strands.
Wire and Insulation Position: All conductor strands must be visible and extend beyond the terminal barrel. The insulation should be compressed but not pierced.
Strand Distribution: All copper strands should be contained neatly within the crimp barrel, with no protruding, missing, or excessively cut wires.
4. The Quality Control Process (How Compliance is Ensured)
Standards are meaningless without rigorous execution:
First-Article Inspection: The "gold standard" for validation. A cross-section of the first crimp from a production batch is analyzed under a microscope. This crimp cross-section analysis checks for uniform conductor compression and full fill of the terminal barrel without voids.
In-Process & Final Audit: Regular checks of crimp height, pull-force, and visual criteria ensure consistent production quality throughout the run.
Tooling & Equipment Control: Mandatory maintenance, calibration, and replacement logs for all crimping machines, dies, and measurement tools are essential for audit trails and consistent wire harness crimping.
Why Xiamen Kehan Electronics Is Your Trusted Wire Harness Partner
For engineers, procurement specialists, and quality managers seeking a truly reliable wire harness supplier, our systematic adherence to international standards is more than a promise—it's a guarantee of performance and partnership.
At Xiamen Kehan Electronics Co., Ltd., we don't just follow standards—we integrate them into every stage of our manufacturing DNA. From rigorous IPC/WHMA-A-620 compliance to specialized automotive-grade crimping certified under LV/USCAR protocols, our process is built to ensure that every cable assembly we deliver meets the highest thresholds of reliability, safety, and consistency.
By choosing Kehan Electronics, you're not just selecting a supplier—you're partnering with a team that speaks the language of quality, understands the criticality of traceability, and is committed to supporting your success in the global marketplace. Let us be your quality-driven, knowledgeable, and dependable link in the supply chain.
Choose Confidence. Choose Kehan Electronics.
How Our Wire Harness Factory Conducts Periodic Pull-Force & Voltage Drop Testing
At our wire harness manufacturing facility, pull-force and voltage drop sampling tests are not random checks. They are a critical part of a statistical process control (SPC) system embedded within our quality management framework. Our goal is proactive defect prevention, not merely final inspection.
1. Core Testing Procedures & Equipment
Pull-Force (Tensile) Testing
Equipment: Calibrated digital pull-force tester.
Method: A crimped terminal assembly is secured in fixtures and pulled axially at a constant speed (typically 25-50 mm/min) until failure. The peak force is recorded.
Pass/Fail Criteria: The measured force must meet or exceed the minimum requirement specified by the relevant standard (e.g., LV214, USCAR) or terminal datasheet. A proper crimp typically results in wire breakage outside the crimp barrel, not pull-out.
Voltage Drop (Contact Resistance) Testing
Equipment: Micro-ohmmeter or 4-wire milliohm meter to eliminate lead resistance error.
Method: A stable DC test current is applied across the crimped connection. The resulting voltage drop is measured and used to evaluate electrical integrity.
Pass/Fail Criteria: The voltage drop must be below the maximum allowable value defined by the application standard. This is the foremost indicator of electrical connection quality in wire harnesses.
2. Sampling Frequency & Strategy (Risk-Based Control)
Our sampling plan is based on statistical principles and risk assessment:
| Production Stage | Sampling Frequency | Rationale & Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| First-Article / Setup Verification | 100% Inspection (initial samples) | Mandatory at shift start, or after any change (tooling, material, operator). This is the highest-risk control point. |
| In-Process Audit | Periodic Sampling (e.g., every 1-2 hours, 2-5 samples) | Monitors process stability and detects drift in crimping machine performance during a production run. |
| Final Lot Acceptance | AQL Sampling (per MIL-STD-1916 or ISO 2859-1) | Provides statistical confidence in lot quality before release. Samples undergo destructive testing. |
| After Process Change | Increased Frequency (revert to first-article level) | Implemented after maintenance, repair, or any anomaly to re-validate the process. |

3. Governing Standards & Specifications
Our test acceptance criteria are hierarchically defined:
Customer-Specific Requirements (Highest Priority): Detailed in drawings or technical agreements.
Industry Standards:
Automotive Wire Harnesses: LV 214, USCAR-21, ISO 8092.
Aerospace: SAE AS50881.
General Assembly Standard: IPC/WHMA-A-620 for visual and mechanical acceptance guidance.
Terminal Manufacturer Datasheet: Provides foundational performance specs for specific wire gauges.
4. Our Commitment to Excellence: Key Practices
Data-Driven SPC: Results are logged in control charts (e.g., X-bar R charts) to identify trends and enable predictive correction, ensuring consistent wire harness reliability.
Closed-Loop Corrective Action (CLCA): Any failure triggers a root cause analysis (RCA) targeting tooling, material, or process, with documented corrective measures.
Calibrated Equipment & Trained Personnel: Test equipment is on a strict calibration schedule. Our technicians are certified in wire harness testing methods and standard interpretation.
For engineers and quality partners, this structured approach to crimp quality validation demonstrates our commitment to delivering reliable cable assemblies that meet the stringent demands of automotive, industrial, and aerospace applications. It transforms a simple test into a guarantee of performance.


